Extend your Copilot - In and outs of Microsoft 365 Copilot Extensibility
Copilot AI
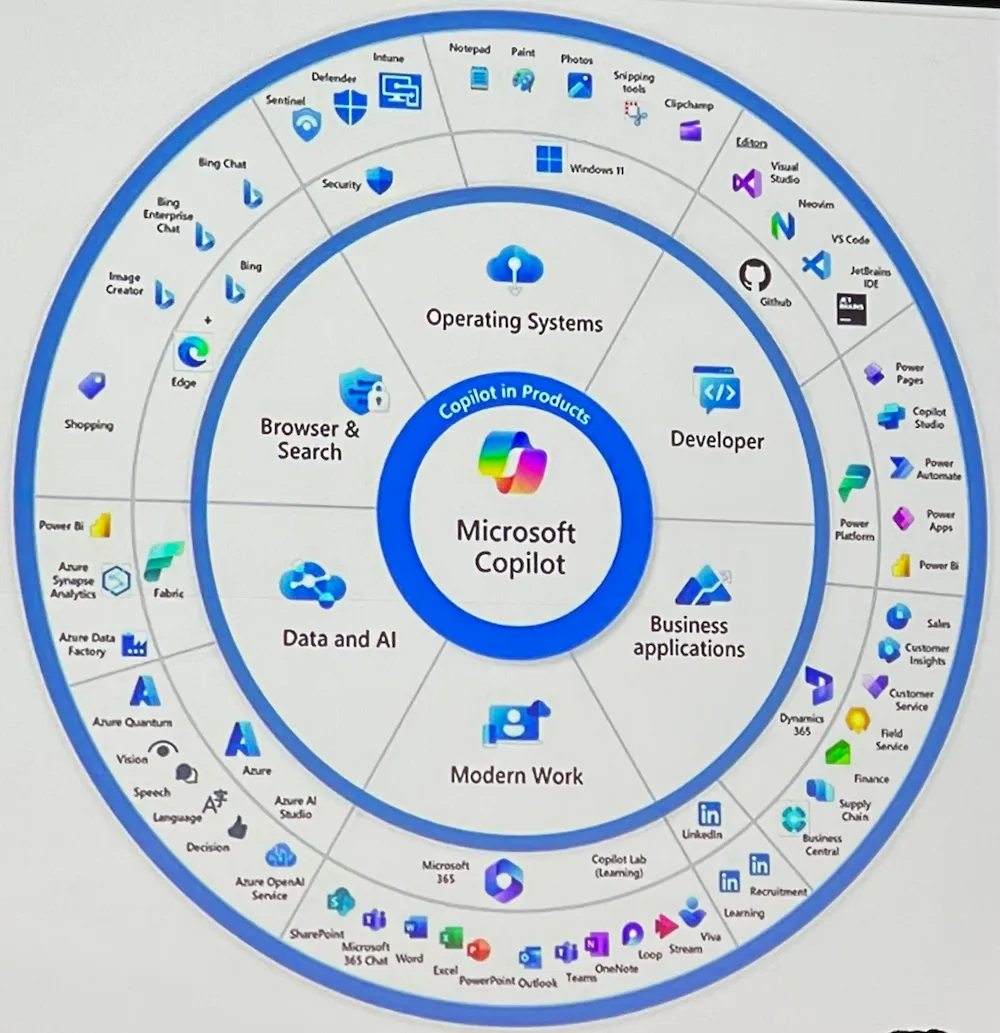
There are 117 different Copilots in the Microsoft ecosystem:
There are some threats coming along with using AI powered tools – categorized into these items:
- Misalignment
- Jailbreaks
- Prompt injections
There are two options to extend Copilot:
- Adding knowledge
Use Graph Connectors to ingest data and content from a 3rd systrem. Think of a search source that provides - Plugins
Ingest live data. They are available in the app store or can be created by yourself
Decide which Copilot extensibility option should be used by considering this decision table (by Stephan Bisser):
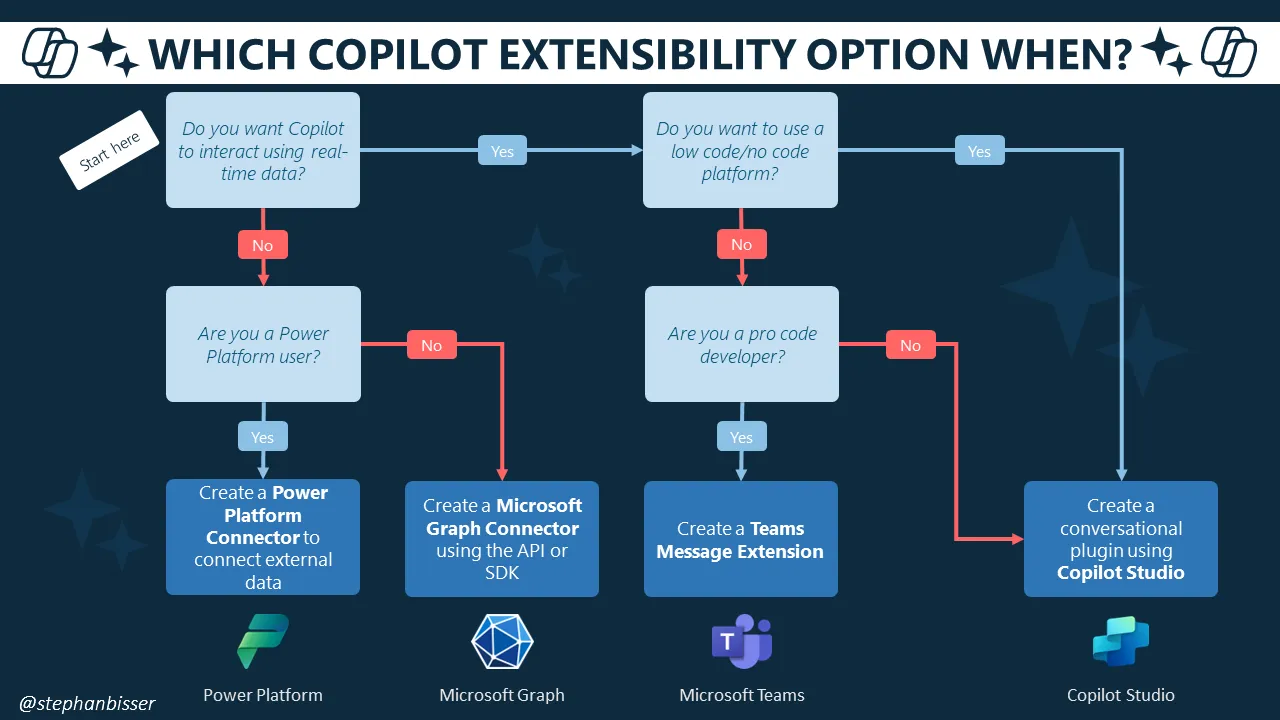
Extensibility
Copilot studio (Live demo)
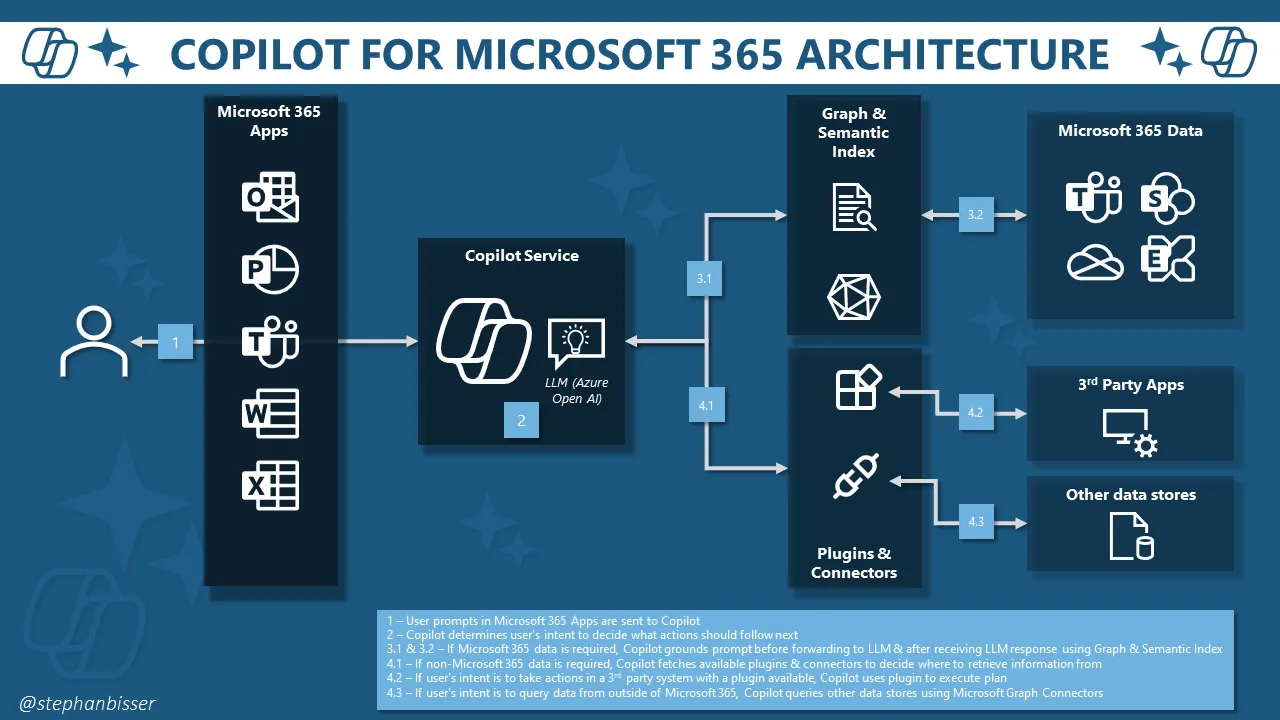
Keep in mind that when building plugins, you always have to set up the «instructions» on the “topic”. The way Copilot plugins work is as follows (by Stephan Bisser):
- User’s prompts in Microsoft 365 Apps are sent to Copilot
- Copilot determines user’s intent to decide what actions should follow next
- If Microsoft 365 data is required, Copilot grounds prompt before forwarding to LLM & after receiving LLM response using Graph & Semantic Index
- If non-Microsoft 365 data is required, Copilot fetches available plugins & connectors to decide where to retrieve information from. If user’s intent is to take actions in a 3rd party system with a plugin available, Copilot uses plugin to execute plan
By writing Graph Connectors, you can implement your onw Copilot data ingestion concept. Keep in mind, that any implementation should always follow some guidelines – and ALWAYS implement acls to take care who can access your data.
Code options
Your implementation is nothing more than a Teams Messaging Extension that returns a result as an Adaptive Card.
By saying this, an appropriate description definition in the manifest (👉 the general description, the commands description and the parameter description) is crucial: the values tell the Copilot engine when to engage this custom extension – and which data comes from the parameters.
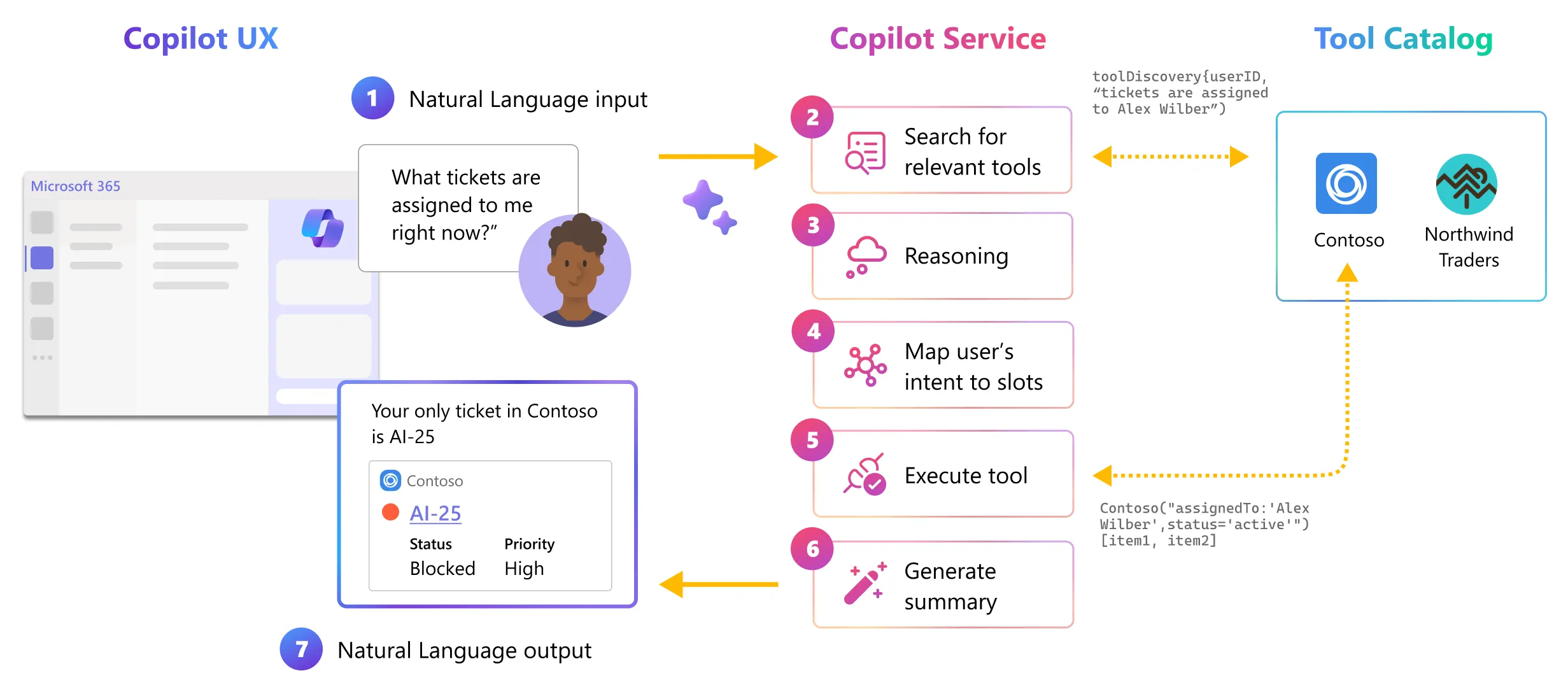
How Copilot for Microsoft 365 decides which plugin to use
Between the end-user’s natural language input to Copilot’s natural language output, the Microsoft Copilot orchestrator works behind the scenes to select and execute the right skill(s) from the right plugin(s) for the end-user’s given task.
The orchestration layer represents the interface between foundation LLMs and the many ways you can extend, enrich, and customize Copilot for the way your customers work.
The following chart illustrates how the Copilot for Microsoft 365 orchestrator selects the right plugin, with the right skill, at the right time, even when there are thousands of options to choose from (see source):
Challenges when building plugins
- Anti-Compete: you never know which other plugins are in use, never use the name of any other plugin in both short and long descripts
- Responsible AI: aviod using inappropriate or offensive keywords
👉 Look for GitHub samples before you start working / coding – and watch the security session from Johann Rehberger