Calling a Custom Prompt from Power Platform's AI Hub
AI Best Practices GPT Development Microsoft 365 Power Platform Software EngineeringCalling a custom prompt from Power Platform’s AI Hub is a two-step process: first, you need to create a custom prompt in the AI Hub, and then you can call it using the API. Using the API, you can pass the input variables to the custom prompt and get the response from the AI model. This sounds simple, but there are a few things you need to consider to make it work.
At the time of writing, the Power Platform AI Hub does not offer a direct way to call a custom prompt via an “external” API. This means that it is probably not intended to call resources from the AI Hub directly from an external application; the AI Hub is designed to be used within the Power Platform environment.
However, you can use an API to call the custom prompt and get the response from the AI model. In this article, I will show you how to call a custom prompt from the AI Hub using the API.
Note
This article is based on the current state of the Power Platform AI Hub. The information provided here may change in the future. Use this information at your own risk.
The scenario
Step 1: Create a custom prompt in the AI Hub
In my (demo) case, I want to call a custom prompt – which is nothing else tha a predefined prompt based on the GPT 4o model – that also can be used for example in a Power Apps Canvas app or a Power Automate flow:
The use case in nutshell: The custom prompt generates a technical report (which can be used as a documentation), based on the JSON structure of a Power Automate workflow. Therefore, we have to pass a JSON object as input to the model. The JSON object should then be analyzed by the model, and the model should return a Markdown report based on the input.
Step 2: Get the GUID of the AI model
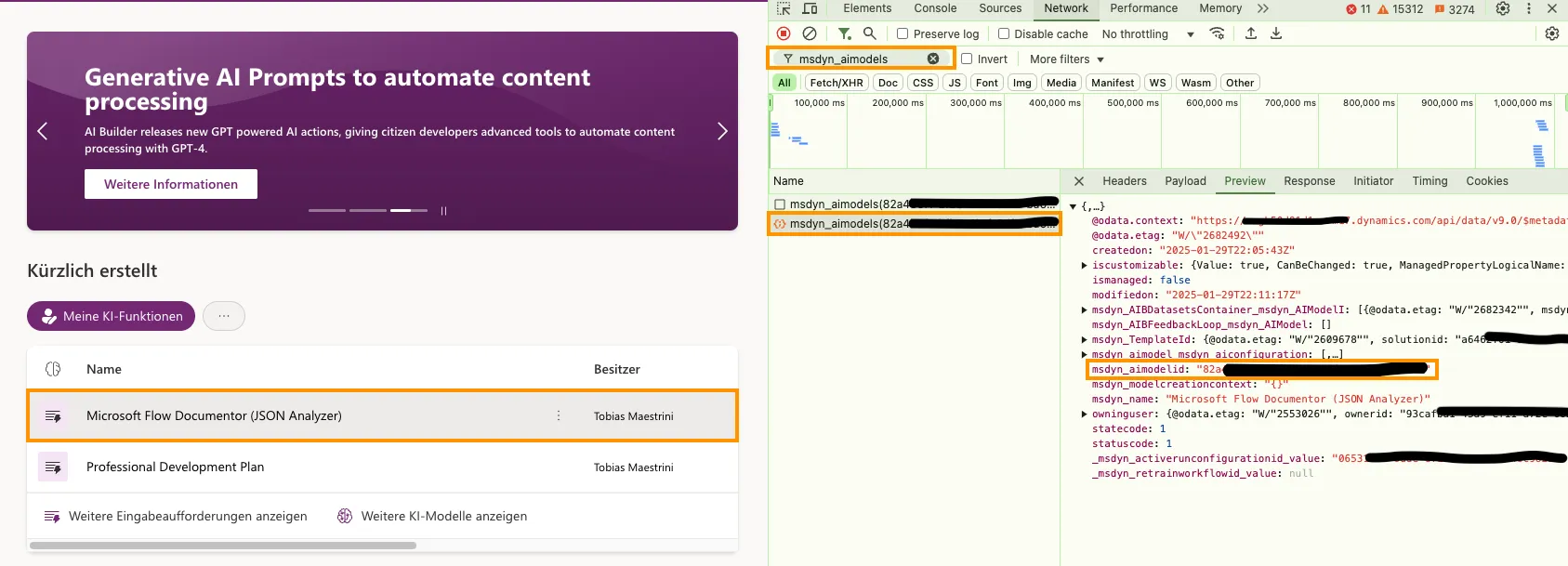
This step is crucial because you need the GUID of the AI model to call the custom prompt using the API. You can get the GUID of the AI model by navigating to the list of your AI models and copying the respective GUID.
If it were that easy, right? Unfortunately, the GUID is not displayed anywhere. Browser’s developer tools to the rescue! Open them and inspect the GUID by using the browser’s developer tools to do some reverse engineering 😃:
- Open the “Network” tab
- Filter the requests by “Fetch / XHR” and by the string that contains “msdyn_aimodels”
- Click on the respective AI model in the list
- Inspect the request (e.g., by clicking on the “Preview” tab) and look for the GUID in the
msdyn_aimodelidparameter
You’re good to go! Now you can call the custom prompt using the API.
Step 3: Call the custom prompt using the API
POST /api/data/v9.0/msdyn_aimodels({{modelId}})/Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.msdyn_PrettyPredict?api-version=2024-05-01 HTTP/1.1
Host: {{environmentUrl}}
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer ey...
{
"version": "2.0",
"simplifiedResponse": true,
"source": "{ \"consumptionSource\": \"PowerApps\", \"partnerSource\": \"AIBuilder\", \"consumptionSourceVersion\": \"PowerFx\" }",
"request": {
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.expando",
<your variables as key-value pairs; ⚠️ values must be strings>
}
}
The Bearer token must include the necessary permissions to call the custom prompt from the AI Hub. Make sure you set the audience claim (aud) to the environment URL of the Power Platform AI Hub where the AI model is deployed (so that it matches the environmentUrl in the request URL).
The request URL
The request URL is structured as follows:
https://{{environmentUrl}}/api/data/v9.0/msdyn_aimodels({{modelId}})/Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.msdyn_PrettyPredict?api-version=2024-05-01
Make sure you replace the placeholders {{environmentUrl}} and {{modelId}} with the values you want to use by pointing to the environment of the Power Platform AI Hub where the AI model is deployed and the GUID of the AI model you want to use, respectively:
environmentUrl- The URL of the environment of the Power Platform AI Hub where the AI model is deployed.
modelId- The GUID of the AI model you want to use; see description below about how to collect this id
The request body
Parameters for the request body:
version- The version of the API you want to use; use 2.0
simplifiedResponse- Whether you want to get a simplified response or not. Set to
falseto receive some extended feedback on the token spend for this request as well as other parameters source- Information about the source of the request; leave it as mentioned above
request- The input variables you want to pass to the custom prompt (along your definition in the prompt itself); 👉 the values always must be strings; objects have to be encoded!
Step 4: Get the response from the AI model
The response from the AI model will be in the following format:
{
"@odata.context": "https://{{environmentUrl}}/api/data/v9.0/$metadata#expando/$entity",
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.expando",
"text": "<the generated text resulting from the model's analysis>",
"finishReason": "stop"
}You’re all set! Use the text property to get the generated text from the AI model.
Also consider the finishReason property, which indicates if the model stopped processing the request for some reason.
Conclusion
Be careful what you do by calling the custom prompt from the AI Hub. This approach does have some limitations, and it doesn’t substitute the use of any AI models that you can call from the Azure stack or other services within a professional development approach.
Also, keep in mind that calling resources from the AI Hub directly from an external application via HTTP API calls is probably not intended by Microsoft. As I already mentioned, the AI Hub is designed to be used within the Power Platform environment.
But it’s still fun to try out how things can be integrated and used in an “alternative way”! 😃